Climate change is defined as changes in average weather patterns. These can be temperature changes (this means that the average temperature changed), more or less rain, etc. A country or a planet’s climate is its average weather patterns.

Table of Contents
- Greenhouse Gases and the Greenhouse Effect
- Causes Of Climate Change
- Cryospheric Impact of Climate Change (glaciers, icecaps, etc)
- Permafrost
- Repercussions: Global Warming Causes More Global Warming
- Carbon Dioxide Information
- Top CO2 Emitters
- FAQ
- Global Cooling and The Sunspot Cycle
- Climate Change Skepticism
- Economic Impact of Climate Change
- Meteorological/Atmospheric Impact Of Climate Change
- Water Shortages
- Droughts
- Article Glossary
Greenhouse Gases And The Greenhouse Effect
Greenhouses gases may be defined as gases which act as insulators, meaning that heat passes through them very slowly/less readily. They are transparent, therefore they allow some sunlight (including some infrared radiation) to pass through them, and then some of that sunlight turns into heat when it reaches the surface of the earth. The rest of the light is reflected by the earth back out into space.
That heat passes back through the greenhouse gases at a much slower pace than the sunlight could enter, so the rate at which heat (remember that it came from sunlight) enters the atmosphere is greater than the rate at which it exits, so this ongoing imbalance causes climate change.
This results in the accumulation of heat, and hence a gradual increase in the Earth’s temperature as time passes. Carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapour are three major greenhouse gases that exacerbate climate change. Greenhouse gases are not harmful at normal levels, but they would cause climate change if there is an excessive amount of them in the atmosphere.
To clarify: CO2, methane, and water vapour are not a problem, but there is much more carbon dioxide in the atmosphere than there normally would be without extensive fossil fuel usage for combustion. This is yet another case of having too much of a good thing. Source.
Greenhouse gases are distributed throughout the atmosphere via winds.
Causes of Climate Change
- Industrial carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions (power plants are an example).
- Transportation CO2 emissions from automobiles, jets, trains, boats and ships.
- Methane emissions from landfills.
- Methane emissions from livestock production.
- Methane emissions from other processes including coal mining.
- Volcanoes emit carbon dioxide.
- Fires (combustion in general) release CO2.
- Melting permafrost (permafrost contains carbon dioxide which is released when melted, click here to learn more).
- Global warming itself.
Cryospheric Impact Of Climate Change
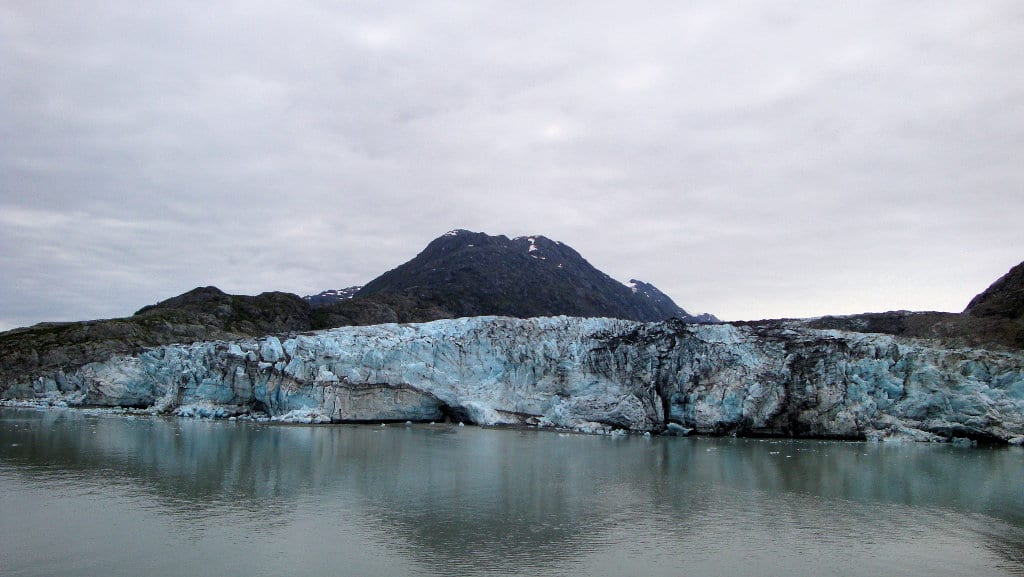
The cryosphere of the earth is defined as the regions where water is perennially frozen, including ice caps, glaciers, permafrost, and ice sheets. In other words, where water is always frozen year round.
Glaciers like the one above are part of the planet’s cryosphere and cover 10% of the world’s land mass, especially in Greenland and Antarctica. Glaciers and ice contain 68% (almost 69%) of all freshwater on earth, and are sometimes relied upon as a source of freshwater when they are melting. [Source]. The water resulting from melting glaciers is then harvested and fed into water supplies.
Glaciers are formed by the accumulation of snowflakes when the rate of snowfall exceeds melting. [In other words, where glaciers are, more snow fell than was melted, so the result of that was accumulation. As more and more snow falls on top of snow, you end up with a larger and larger heap (also heavier) of snow and the heavy weight of the snow on top compresses the snow at the bottom, and then it itself is eventually compressed as more snow falls onto it as well. [Source].
An interesting fact about glaciers is that as a water source, they are very resistant to pollution compared to liquid water because ice cannot be penetrated as easily. To pollute water, all you need to do is basically throw pollutants into it, the surface of glaciers can be contaminated but almost all of the ice is below the surface.
Now the opposite is taking place where glaciers are retreating (shrinking) because of climate change/global warming, so the glaciers melt faster than snow accumulates on them.
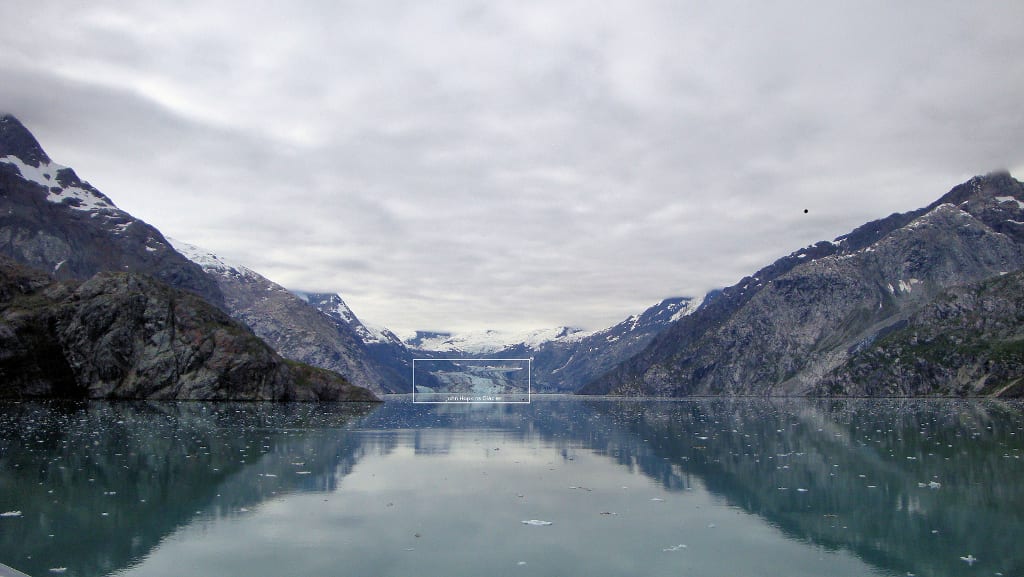

Image obtained with thanks from Thom Watson on Flickr.
Sometimes you have to look a bit more closely to see glaciers like the type in the rectangle above. There are many different types, sizes, and shapes of glaciers which can be as small as a football field sized patch or up to 161 km (100 miles) long.
Permafrost
Permafrost is ground/soil which is perennially frozen for at least two years. It normally exists at high latitudes and higher elevations. Melting permafrost can contribute significantly to climate change by releasing the greenhouse gases trapped in the ice.
Permafrost in Northeastern Siberia contains enough carbon dioxide to cause another 75 years of climate change all on its own. That is 75 times the carbon dioxide emissions of fossil-fueled power plants. If it melts, it will release that CO2 and may exacerbate climate change dramatically.
Note: A high latitude means either far north or far south of the equator (on a map this is how many degrees north or south of the equator), don’t confuse this with elevation which is height above a fixed reference point off the surface of the earth. The reference point mentioned is the center of the earth. The equator is 0°. 10° north means 10 degrees above of the equator and 10° south means 10 degrees below the equator.
Repercussions: Climate Change Ends Up Causing More Climate Change
Global warming causes disasters and other events which contribute to global warming themselves such as:
- Drought: Drought is dry weather that causes wildfires which burn trees which contain carbon which then becomes carbon dioxide when burnt to be released into the atmosphere.
- Climate warming causes permafrost to melt and release the carbon dioxide it contains into the atmosphere.
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
Carbon dioxide is absorbed by a variety of sources, some of which include all plants and the ocean. It is also produced by a variety of sources, including volcanoes, animal and human exhalation, combustion of carbon containing material. As carbon dioxide is one of the main causes of climate change, I provided details about it below.
Density of carbon dioxide as a gas: 1.977 g/L.
0.50581689428 litres per gram.
To determine how many litres a certain mass of carbon dioxide would be, multiply the figure in grams by the litres per gram figure above.
10 litres = 19.77 grams.
100 litres = 197.7 grams.
1,000 litres = 1977 grams.
Global Carbon Dioxide (CO2) Concentration Level
Top CO2 emitters in Order of Emissions – Worldwide
Fossil Fuels
- Power: 10,539 Mt/Year (Mt/Year = Million Tonnes per Year).
- Cement Production: 932 Mt/Year.
- Refineries: 798 Mt/Year.
- Iron and Steel Industry: 646 Mt/Year.
- Petrochemical Industry: 379 Mt/Year.
- Oil and Gas Processing: 50 Mt/Year.
- Other Sources: 33 Mt/Year.
Biomass
- Bioethanol and bioenergy: 91 Mt/Year.
Total: 13,466 Mt/Year. Source.
CO2 Emissions By Source (percentage of fossil fuel caused emissions that each of the following accounts for)
Transportation (World): 22%. Source.
Electricity Generation (U.S): 40% (2004) Source: Page 9 – PDF.
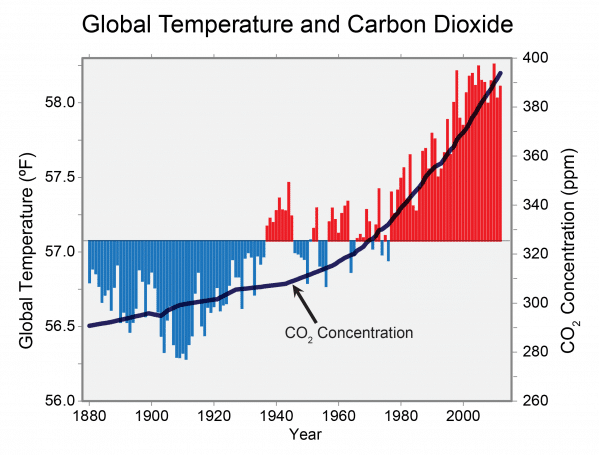
The graph above is one about the close relationship between temperature and atmospheric carbon dioxide during the past few hundred thousand years. There are points on the graph at which they don’t correlate as much as the other parts of the graph, but that may have been due to other causes or greenhouse gases. Carbon dioxide is one of many.
A Short FAQ
- Is carbon dioxide harmful? How harmful is it to public health and the environment overall?
No, CO2 is a harmless natural compound which is an important part of the carbon cycle, but excessive amounts of any compound can have undesirable consequences such as excessive global warming. Excessive amounts of carbon dioxide cause global warming because it is a greenhouse gas.
- Where does carbon dioxide come from?
Carbon dioxide comes from a variety of sources, including exhalation of animals and humans, as well as volcanoes, combustion of carbon containing items, and decomposition.
- What is the atmospheric lifespan of carbon dioxide?
The lifespan of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is >50 years. Source – PDF.
Global Cooling And The Sunspot Cycle
When studying climate change, what matters most is not what the temperature is at the moment, nor temporary spikes or dips in average global temperature but the most consistent pattern that temperature follows, and of course how consistent that pattern is. If it shows that the earth’s temperature is following an upward trend most of the time, then that deserves attention and further research. That is what brought attention to global warming, creating the foundation for a new sector of climate science.
Some global warming skeptics claimed that the earth cooled after 2005, but the sunspot cycle happened to be winding down during the same time period. This misunderstanding undermined the credibility of climate science.
The sunspot cycle may be the reason why the weather was so hot in 2005, and the hurricane season for that year was unusually active in the Atlantic. For those that don’t know, hurricanes are partly fueled by heat.
Sunspots Increase Temperatures
Sunspots are dark areas in the sun whose temperatures can drop to 3,700 K or 3,426 °C which is 6,200 °F. Source. Sunspots make the sun appear slightly brighter. Especially the area surrounding them known as the faculae. Source.
Even though sunspots are dark spots on the sun, they actually cause an increase in net solar radiation and the earth’s temperature, according to an expert from the University of Wyoming. Source.
Economic Impact Of Climate Change
A less frequently discussed topic is the economic impact of climate change. Global warming causes drought, flooding, water shortages due to accelerated glacial melting (please visit the water shortages section below) as well as drought, which also have their own economic impact.
Science (and of course, basic observation) has shown that drought causes water shortages, due to the fact that rain is a very significant source of water, it either flows into rivers above or underground. Rivers are a significant source of freshwater almost everywhere and freshwater is required to water crops.
A lack of water entails a shortfall in food supply and this means that less food can be produced for resale. The main consequence of this is that food producers don’t make as much money, so that is a financial loss to them. It also causes food prices to increase which costs consumers money. You can learn more about drought on this page.
Crop shortages also entail meat shortages because animals are usually fed with some form of vegetation.
An economic repercussion of more expensive food means that people have to spend a greater percentage of their money on food, therefore, people will have less money to spend on everything else and will have to cut back on less important items. When people spend less money, businesses do not make as much money, and hence lay off people if sales decrease significantly enough.
Atmospheric Impact Of Climate Change
This section pertains to the effect that excessive greenhouse gas emissions may or do have on the weather and climate.
Precipitation/Rain
Why it rains and how climate change can affect rainfall (and snowfall):
Learn how precipitation works.
Global warming can cause increased precipitation because it causes temperature increases, and as I said on the precipitation page, heat is what starts and partially drives the rain formation process by causing water to evaporate.
More heat equals more evaporation, and that means that more water vapour will enter the cold area mentioned up in the atmosphere, and more water vapour translates to more condensation, which equals more clouds, and finally, more precipitation. Snow comes from clouds as well, snow is precipitation. During the winter, increased water temperatures can lead to increased snowfall, which puzzles many people when there is record snowfall, despite the warming caused by climate change.
Water Shortages
Glaciers melt into rivers and are often one of their significant sources of water, apart from rain. If they melt too quickly, then they will no longer be available as a freshwater supply in the future. This is a problem especially for areas far inland of large countries (far from the ocean) due to the fact that the alternative to freshwater is normally desalination.
Droughts
Climate change causes droughts which affect the water supply in affected areas as well as agriculture negatively. Read more on the drought page.
Article Glossary
Perennial: Lasting throughout the entire year.





